Lecture 10: Useful libraries in Python (Solution)#
Sympy (Symbolic notations)
Scipy (optimize)
Fsolve (Linear and Nonlinear equations)
Curve fitting
Solving ordinary differential equations#
Sympy to solve some ODE examples. To use Sympy, we first need to import it and call init_printing() to get nicely typeset equations
import sympy
from sympy import symbols, Eq, Derivative, init_printing, Function, dsolve, exp, classify_ode, checkodesol
# This initialises pretty printing
init_printing()
from IPython.display import display
# Support for interactive plots
from ipywidgets import interact
# This command makes plots appear inside the browser window
%matplotlib inline
Example: car breaking#
During braking a car’s velocity is given by \(v = v_{0} e^{−t/\tau}\). Calculate the distance travelled.
We first define the symbols in the equation (\(t\), \(\tau\) and \(v_{0}\)), and the function (\(x\), for the displacement):
t, tau, v0 = symbols("t tau v0")
x = Function("x")
Next, we define the differential equation, and print it to the screen for checking:
eqn = Eq(Derivative(x(t), t), v0*exp(-t/(tau)))
display(eqn)
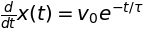
The dsolve function solves the differential equation symbolically:
x = dsolve(eqn, x(t))
display(x)
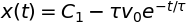
where \(C_{1}\) is a constant. As expected for a first-order equation, there is one constant.
SymPy is not yet very good at eliminating constants from initial conditions, so we will do this manually assuming that \(x = 0\) and \(t = 0\):
x = x.subs('C1', v0*tau)
display(x)
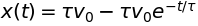
Specifying a value for \(v_{0}\), we create an interactive plot of \(x\) as a function of the parameter \(\tau\):
x = x.subs(v0, 100)
def plot(τ=1.0):
x1 = x.subs(tau, τ)
# Plot position vs time
sympy.plot(x1.args[1], (t, 0.0, 10.0), xlabel="time", ylabel="position");
interact(plot, τ=(0.0, 10, 0.2));
Scipy Optimize#
Bisection#
Find root of a function within an interval using bisection.
Basic bisection routine to find a zero of the function f between the arguments a and b. f(a) and f(b) cannot have the same signs.
from scipy import optimize
# Define a function
def f(x):
return (x**2 - 1)
root = optimize.bisect(f, 0, 2)
print("The root of the function: {}".format(root))
The root of the function: 1.0
Newton Raphson#
Find a zero of the function func given a nearby starting point x0.
from scipy import optimize
# Define a function
def f(x):
return (x**3 - 1) # only one real root at x = 1
root = optimize.newton(f, 1.5)
print("The root of the function: {}".format(root))
The root of the function: 1.0000000000000016
Systems of equations#
Linear equations#
System of m equations \((i = 1, \dots, m)\) in \(n\) unknowns \(x_j \quad (j = 1, \dots, n)\) can be represented as \(Ax = b\). For example,
To solve a linear system of equations, we will use numpy.linalg.solve, which requires a matrix \(A\) and a vector \(b\) as arguments.
import numpy as np
# Define the matrix A and vector b
A = np.array([[1, 2], [-3, 4]])
b = np.array([5, -20])
# Solve the system of linear equations
x = np.linalg.solve(A, b)
print("The solution x: {}".format(x))
The solution x: [ 6. -0.5]
Non-linear equations#
Solving a system of non-linear equations:
We need to rearrange each equation such that we have 0 on the right-hand side.
Non-linear system of equations can be solved using scipy.optimize.fsolve
from scipy.optimize import fsolve
import math
# z is a vector collecting x1 and x2
def equations(z):
x1, x2 = z
return (x1+x2**2 -4, math.exp(x1) + x1 * x2 - 3)
x1, x2 = fsolve(equations, (1, 1))
print("x1 is {:.3f}, x2 is {:.3f}".format(x1, x2))
print("Check if the solution for f(z) = 0")
print(equations((x1, x2)))
x1 is 0.620, x2 is 1.838
Check if the solution for f(z) = 0
(4.4508396968012676e-11, -1.0512035686360832e-11)
Curve fitting#
Linear and polynomial fits with np.polyfit
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.array([5, 10,20,30,50])
y = np.array([3.3, 11.2, 19.5, 21.8, 42.3])
plt.plot(x, y, 'or')
plt.axis([0 , 60, 0 , 60])
plt.show()
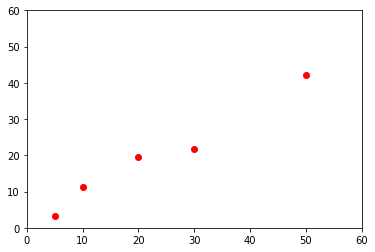
# Fit a straight line through points
x = np.array([5, 10,20,30,50])
y = np.array([3.3, 11.2, 19.5, 21.8, 42.3])
# coefficients
coeffs = np.polyfit(x, y, 1)
polynomial = np.poly1d(coeffs)
print("The polynomial is: {}".format(polynomial))
print("Regression coefficients are: {}".format(coeffs))
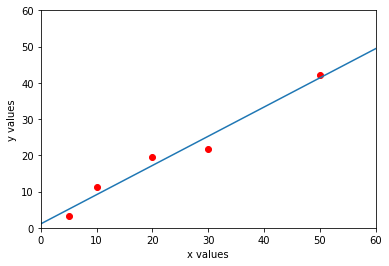
The polynomial is:
0.8056 x + 1.091
Regression coefficients are: [0.805625 1.090625]
# Plot the fit
xp = np.linspace(0,60,100)
plt.plot(x, y, 'or', xp, polynomial(xp), '-')
plt.axis([0 , 60, 0 , 60])
plt.xlabel('x values')
plt.ylabel('y values')
plt.show()
# Fit a cubic polynomial
x = np.array([5, 10,20,30,50])
y = np.array([3.3, 11.2, 19.5, 21.8, 42.3])
# coefficients
coeffs = np.polyfit(x, y, 3)
polynomial = np.poly1d(coeffs)
# Plot the fit
xp = np.linspace(0,60,100)
plt.plot(x, y, 'or', xp, polynomial(xp), '-')
plt.axis([0 , 60, 0 , 60])
plt.xlabel('x values')
plt.ylabel('y values')
plt.show()
print(polynomial)
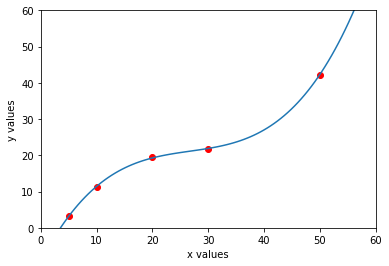
3 2
0.001282 x - 0.1029 x + 2.973 x - 9.272
